Are you searching for WAEC Agricultural science questions and answers 2022? waec agricultural science past questions 2022? WAEC Agric past questions and answers PDF? If yes, then your search ends here. Kindly find below the WAEC Agricultural science questions and answers 2022.
Related Post:
WASSCE 2022 AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE 1 OBJECTIVE TEST
1. To reduce rural-urban migration, the government should
A. establish commodity boards.
B. provide social infrastructure.
C. establish tractor-hiring units.
D. provide extension services to farmers.
2. The establishment of cooperative farming is encouraged by governments because it
A. enables farmers to control soil erosion.
B. flicilitates the use of hand tools.
C. enables individual farmers to acquire capital.
D. allows farmers to cultivate small and scattered plots.
3. A non-governmental organization involved in agricultural development in West Africa is
A. Operation Feed the Nation
B. River Basin Development Authority
C. Agricultural Development Authority.
D. International Institute of Tropical Agriculture
The diagram below illustrates a farm implement. Use it to answer questions 4, 5 and 6.
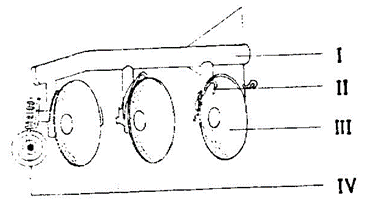
4. The illustrated farm implement is used for
A. pulverizing soil into fine tilth
B. breaking up soil into clods.
C. gathering topsoil.
D. levelling soil surface
5. The part of the illustrated farm implement which enables it to roll over obstacles is labelled
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
6. The functions of the part labelled II is to
A. remove soil
B. turn sod.
C. break clods.
D. cut stomps.
7. A combine harveter can be used simultaneously to harvest
A. legtirnes and apply fertilizer
B. grains and eradicate weeds.
C. tuber and distribute fertilizer.
D. cereals and winnow grains
8. Ranging poles used in farm surveying have characteristic
A. green and white bands.
B. Blue and white bands.
C. red and white bands.
D. black and red bands.
9. Decomposition of soil organic matter is mainly caused by
A. Bacteria.
B. Algae
C. fungi.
D. nematode
10. The main Ciictors responsible for rock weathering in the desert are high temperature and
A. annual activity,
B. water
C. wind
D. root growth.
11. A difference between physical and chemical weathering is that
A. there is a change in the mineral composition of rock in physical weathering.
B. the mineral composition of rock is changed in chemical weathering.
C. carbonation is necessary in physical weathering.
D. wind is necessary in chemical weathering.
Use the information below to answer questions 12 and 13.
In an experiment on soil porosity, the following results were obtained:
Volume of dry soil = 52 cm3
Volume of water = 48 cm3
Volume of soil and water = 78cm3
12. Determine the volume of airspace in the soil sample.
A. 22cm3
B. 26cm3
C. 30cm3
D. 100cm3
13. Calculate the porosity of the soil sample.
D. 100 cur’
13. Calculate the porosity of the soil sample.
A. 28.21 %
B. 43.31%.
C. 45.83%
D. 61.54%
The diagram below illustrates a tool used to analyze a soil sample in an experiment. Use it to answer questions 14, 15 and 16.
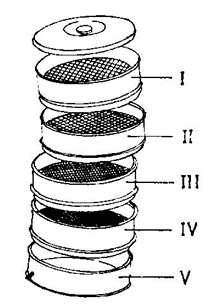
14. The aim of the experiment is to determine the soil
A. structure.
B. texture.
C. mineral matter.
D. organic matter.
15. The part labelled III will contain
A. clay.
B. silt.
C. coarse sand.
D. fine sand.
16. The diameter of the soil particle that would be retained in the part labelled II is
A. 0.002 – 0.02 mm.
B. 0.02 – 0.2 mm.
C. 0.2 – 2.0 mm.
D. > 2.0 mm.
17. Potassium deficiency in cereal crops is indicated by
A. browning of leaves from the tips and margins.
B. yellowing of younger leaves.
C. purpling of leaves.
D. white and irregular spots on leaves.
18. Nitrogen is important in plants because it is mainly needed in
A. fruit formation.
B. root development.
C. leaf formation.
D. cell division.
19. Water can be conserved in the soil by
A. mulching, strip cropping and cover cropping.
B. weeding, strip cropping and c lean clearing.
C. clean clearing, mulching and strip cropping.
D. cover cropping, mulching and weeding.
20. Monocotyledonous crops include
A. oil palm, rice and plantain.
B. cowpea. pepper and tomato.
C. garden egg. cassava and mango.
D. rubber, cashew and orange.
21. Swampy lands are most suitable for growing
A. yam
B. ice.
C. maize.
D. tomato.
22. If maize seeds are sown at a spacing of 60 cm by 90 cm, what is the plant population of maize expected on one hectare of farmland?
A. 18.519 plants
B. 16.667 plants
C. 11,111 plants
D. 5.400 plants
23. The practice of placing the correct number of seeds in the soil with definite intra-row and inter-row spacing is called
A. seed drilling.
B. centrifugal distribution.
C. precision planting.
D. seed broadcasting.
24. Which of the following groups of crops will thrive in areas with high rainfall?
A. Cotton, coNlpea and groundnut
B. Millet, maize and cotton
C. Guinea corn. cowpea and maize
D. Cocoa, oil palm and rubber
The diagram below illustrates a crop. Use it to answer questions 25, 26 and 27.

25. The illustrated crop is
A. Capsicum fruiescenc
B. .4 belmascus escuktitus.
C. Glycine max.
D. Hey ea brasiliensis.
26. A disease that could affect the illustrated crop is
A. swollen shoot.
B. smut.
C. root knot.
D. rosette.
27. The most suitable fertilizer for the production of the illustrated crop is
A. muriate of potash.
B. ammonium sulphate.
C. potassium nitrate.
D. single superphosphate
28. Capping is a cultural practice carried out in the cultivation of
A. carrot.
B. cassava.
C. potato.
D. yam.
29. Damping off disease of tomato could be controlled by
A. staking.
B. supplying.
C. thinning.
D. pruning.
30. The most common way of controlling weeds in tree crop plantations is by
A. crop rotation.
B. hand pulling.
C. flooding.
D. slashing
31. Which of the following crops is correctly matched with a disease that affects it?
A. Maize – smut
B. Sorghum – scab
C. Rice black arm
D. Yam – blast
32. Soil-borne diseases could be controlled in the nursery by
A. mulching.
B. manuring.
C. heat treatment.
D. provision of shade.
Use the information below to answer question 33.
- I. Yellowing of leaves
- II. Raised brown spots on the leaves
- III. Drying up of leaves
- IV. Exudation of gum
33. The disease of citrus described above is
A. die-back.
B. gummosis.
C. tristeza.
D. blight.
The diagram below illustrates the digestive system of a farm animal. Use it to answer questions 34, 35 and 36.

34. The diagram illustrates the digestive system of a
A. chicken.
B. turkey.
C. sheep.
D. rabbit.
35. The part labelled III is the
A. pancreas.
B. caecum.
C. small intestine.
D. large intestine.
36. Digestion of fats takes place in the part labelled
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
37. Lactation normally occurs
A. at the onset of conception.
B. at the onset of puberty
C. after gestation.
D. after mating.
38. A by-product of all livestock is
A. hide.
B. horn.
C. milk.
D. meat.
39. Removal of needle teeth is important in the management of
A. kids.
B. lambs.
C. calves.
D. piglets.
40. Which of the following farm animals will browse more on plants in a pasture?
A. Goats
B. Cattle
C. Pigs
D. Sheep
41. The main reason for castrating farm animals is to
A. remove male odour.
B. make the animal sterile.
C. increase meat production.
D. make them lose weight.
42. Which of the following statements about silage are true? it
I. has laxative effect
II. is acidic in reaction
III. has a strong aroma when well prepared
A. Land II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
43. If 200 layers require 25 kg of layer mash per day, calculate the quantity of-teed required by 1,000 layers per day.
A. 5kg
B. 40kg
C. 80kg
D. 125kg
44. Salt licks are provided for grazing animals to
A. make the pasture palatable.
B. supply nutrients in pastures.
C. supplement mineral intake.
D. provide laxatives.
45. The correct order of arrangement of ration for piglets from day old is
A. weaners → growers → creep → finisher.
B. creep → weaners → growers → finisher.
C. growers → finisher → creep → weaners.
D. finisher → creep → weaners → growers.
46. In farming enterprise, short term loans are used
A. purchase farm machinery.
B. construct new farm buildings.
C. construct an irrigation dam.
D.. purchase agrochemicals.
The table below illustrates a farm record for Goodness Farms in the year 1970. Use it to answer questions 47. 48 and 49.
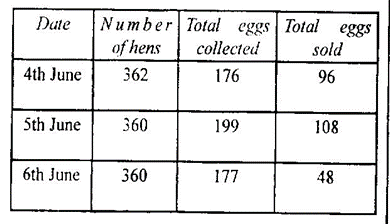
47. The table illustrates
A. an inventory record.
B. a product ion record.
C. a labour record.
D. an input record.
48. Calculate the total amount of eggs sold on the farm.
A. 804
B. 552
C. 300
D. 252
49. If all the unsold eggs were later sold on 7th June at N5.00 per crate. calculate the income from unsold eggs. (Assuming a crate = 30 eggs)
A. N40.00
B. N45.00
C. N50.00
D. N55.00
50. The gross profit of a farm business is the farm’s
A. net sales less cost of production.
B. total sales less operating expenses.
C. net sales less taxation.
D. total sales less cost of production.
WAEC Agricultural science questions and answers 2022 THEORY ANSWERS
1. (a) Reasons why government should enact laws to regulate the use of land for agriculture
- Encourage enterprising farmers acquire land for agriculture.
- Ensure proper use of agricultural land
- Prevent land fragmentation which discourages large scale farming
- Safeguard farmers against unreasonable eviction /land grabbing
- Facilitate government programmes/schemes like Green Revolution which requires large expanse of farmland
- Reduce litigation on lands/land disputes
- Encourage the production of certain farm produce
- Facilitate land improvement programmes like irrigation, drainage, dams Encourage commercial agriculture.
- Encourage the acquisition of certificate of occupancy (C of 0)/title deed/security of tenure
(b) (i) Most appropriate type of farm power to use for tillage operations on the cocoa farmland
- Mechanical power
(ii) Reasons for using mechanical power on the cocoa farmland
- – Saves labour/makes labour available for other farm operations
- – Reduces drudgery/make tillage operation less tedious
- – Saves time/timeliness of tillage operations/faster
- – Reduces the cost of operation/cost effective
- – Reduces health hazards
- – Makes it possible to cultivate large hectares of farmland
- – More efficient
(c) Functions of the following parts of a seed planter
(i) Seed tube
– Directs seeds from the base of the hopper into the soil
(ii) Furrow opener
– Digs hole in front of the seed drill into which the seeds drop
(iii) Hopper
– Contains/keeps the seeds to be planted
(iv) Seed metering device
– Regulates the dropping of seeds from the seed box/hopper into the seed tube
(v) Furrow wheel
– Presses the soil to cover the seeds dropped in the hole
(d) Machines used in processing crops after harvesting
- – Thresher
- – Combine harvester
- – Sheller
- – Grinder
- – Grain dryer
- – Mixer
- – Palm kernel cracker
- – Rice poliSher
- – Straw Chopper
- – Winnowing machine
- – Press/Hydraulic press
- – Mill/hammer mill
- – Decorticator Grater
- – Blender
- – Juice extractor
- – Rice huller
- – Bailer
- – Ring macerator
- – Sterilizer
2. (a) Explain of the following cropping systems
(i) Monocropping
- – This is the cultivation of only one type of crop on a piece of land at a given time
- – The crop is harvested before another crop is planted
- – The soil nutrients for the crop may be exhausted
(ii) Mixed cropping
- This refers to the cultivation of two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land at the same time
- Guards against crop failure
- Ensures effective use of soil nutrients
- It is practised where land is scarce
(iii) Mixed farming
This refers to the cultivation of crops and rearing of farm animals on the same piece of land at the same time.
Reduces cost of production
Crop residues serve as feed for farm animals.
Animal dung serves as organic manure for the crops.
(iv) Crop rotation
- This is the cultivation of different crops on the same piece of land in a definite sequence from year to year.
- Improves soil fertility
- Checks pests and disease
b(i) Nutrient deficient in the orange plants
Phosphorus
(ii) Inorganic fertilizers that could correct phosphorus deficiency observed in the orange plants
- Basic slag
- Dicalcium phosphate
- Diammonium phosphate
- Single superphosphate
- Triple superphosphate
- Ammonium polyphosphate liquid
- NPK fertilizer
- Mono-ammonium phosphate
- Rock phosphate
(c) Materials that could be used to attract bees to a new beehive
- – Raffia wine
- – Locust beans
- – Honey bee wax
- – Coco beans juice
- – Palm’s, wine/sweet syrup
- – Bait hive/swam trap
- – Old frame with bee comb
- – Dry cassava flour
- – Pineapple juice
- – Lemon grass essential oil
- – Molasses
- – Quercetin chemicals Sugar
- – Mango juice
- – Propolis
- – Pheromone lures
3. (a) Explanation of causes of damage to maize during storage
(i) High humidity
– High humidity often leads to mould formation, thus reducing the quality of maize
(ii) Pests
- – The presence of pests reduces the quality of maize
- – Pests reduces the quantity of maize
- – Reduces the viability of seeds ; thus the germination rate
(iii) Pathogens
– The presence of moulds and other fungi reduces the quality of stored maize
(iv) Heat generated during storage
– This enhances the formation of moulds, thus reducing the quality of maize
(v) Poor Storage Structure:
– Leaking roof allows water to get into the stored maize; thus leading to mouldiness
– Allows infestation of pests and pathogens
(b) (i) Possible offspring that could result from the cross

(ii) I. Genotypic ratio of the offspring
- 1:2:1
II. Phenotypic ratio of the offspring
- 3:1
c) Mende ‘s laws of inheritance
First law (Law of segregation of genes)
Genes ace in pairs and are transmitted independently from one generation to another
Second law (Law of independent assortment of genes)
Genes for different traits are sorted separately from one another such that the inheritance of one trait is not dependent on another
(d) Forage grasses
- – Guinea grass/Panicum maximum
- – Elephant grass/Pennisetum purpureum
- – Southern gamba grass/ Andropogon tectorum
- – Bermuda grass/Bahana grass/Cynodon dactylon
- – Carpet grass/Axonopus compressus
- – Northern gamba grass/Andropogon gayana
- – Stubborn grass/Eleusine indica
- – Giant star grassICynodon plectostachyus
- – Rhodes grassIChloris gayana
- – Spear grass/Imperata cylindrica
- – Kikuyu grass/Pennisetum clandestinum
4. (a) Table
(b) Calculation on the stocking density of broilers
- Length of deep litter house = 36 m
- Breadth of deep litter house = 10m
- Area of deep litter house = Length x Breadth
- = 36 mx10m
- = 360m2
For further information visit: www.waeconline.org.ng

